Kivy: Liste des éléments graphiques
De Centre de Ressources Numériques - Labomedia
(Redirigé depuis 5 Kivy: Liste des éléments graphiques)
Remarques:
- Les éléments graphiques sont définis dans un *.kv, et non dans le main.py. La doc kivy, c'est expliquer la factorisation avec un exemple du genre y = a * (sin(x) + ln(x)) à un élève de 5ème !
- Pour construire une application installable sur Android avec Buildozer, le fichier principal doit s'appeler main.py. Dans les exemples ici, ils ont un nom explicite pour s'y retrouver.
- Testé sous Linux Mint 17 et python 3.4.
- C'est du python, BoxLayout n'a rien à voir avec Boxlayout
- Les titres pointent vers la documentation officielle. Les fichiers contiennent kivycatalog, showcase, ping_pong et widgets.
Sommaire
Les fichiers sur Github et en zip
- Cloner le git ou télécharger le zip.
- Ouvrir un terminal dans le dossier.
- python3 je_teste.py
ou
Dans geany, ouvrir tous les fichiers et Excécuter les .py
Liste des éléments graphiques kivy.uix
- Liste des widgets Tous les éléments à votre disposition.
- Programming Guide Kv language
- Kivy Language
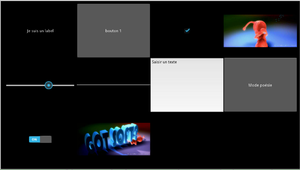
Widgets classiques pour interface utilisateur
Label
Button
CheckBox
Image
Slider
Progress Bar
Text Input
Toggle button
Switch
Video
classique.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import kivy
kivy.require('1.8.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (1120, 630)
class ClassiqueApp(App):
def build(FloatLayout):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
ClassiqueApp().run()
classique.kv
#:kivy 1.8.0
GridLayout:
cols: 4
rows: 3
padding: 10
Label:
text: "Je suis un label"
Button:
text: "bouton 1"
CheckBox:
active: True
Image:
source: 'softboy.png'
Slider:
min: -100
max: 100
value: 25
ProgressBar:
min: 0
max: 1000
TextInput:
text: "Saisir un texte"
ToggleButton:
text: "Mode poésie"
Switch:
active: True
Video:
source: "softboy.avi"
play: True
Layouts: Méthodes de dispositions des éléments graphiques
Ressources
- Anchor Layout
- Box Layout
- Float Layout
- Grid Layout
- Page Layout
- Relative Layout
- Scatter Layout
- Stack Layout
AnchorLayout
 Les éléments sont ancrés sur un point
Les éléments sont ancrés sur un point
anchorlayout.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import kivy
kivy.require('1.8.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (1120, 630)
class AnchorlayoutApp(App):
def build(FloatLayout):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
AnchorlayoutApp().run()
anchorlayout.kv
#:kivy 1.8.0
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'right'
anchor_y: 'bottom'
padding: 50
Button:
size_hint: 0.3, 0.4
text: "bouton 1"
Label:
size_hint: 0.7, 0.6
text: "Je suis ancré"
BoxLayout
 Empilement de boîtes horizontales ou verticales.
Empilement de boîtes horizontales ou verticales.
boxlayout.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import kivy
kivy.require('1.8.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (1120, 630)
class BoxlayoutApp(App):
def build(FloatLayout):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
BoxlayoutApp().run()
boxlayout.kv
#:kivy 1.8.0
BoxLayout:
spacing: 10
padding: 10
orientation: "horizontal"
Button:
text: "bouton 1"
Button:
text: "bouton 2"
Button:
size_hint_y: 0.3
text: "bouton 3"
BoxLayout:
spacing: 10
padding: 10
orientation: "vertical"
Button:
size_hint_y: 0.5
text: "bouton 4"
Button:
size_hint_y: 0.4
text: "bouton 5"
Button:
size_hint_y: 0.3
text: "bouton 6"
Button:
text: "bouton 7"
FloatLayout
GridLayout
 Défini une grille avec des lignes et des colonnes.
Défini une grille avec des lignes et des colonnes.
gridlayout.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import kivy
kivy.require('1.8.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (1120, 630)
class GridlayoutApp(App):
def build(FloatLayout):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
GridlayoutApp().run()
gridlayout.kv
#:kivy 1.8.0
GridLayout:
spacing: 10
padding: 10
cols: 2
rows: 2
Button:
text: "bouton 1"
Button:
text: "bouton 2"
Button:
text: "bouton 3"
GridLayout:
spacing: 10
padding: 10
cols: 2
rows: 2
Button:
size_hint_y: 0.5
text: "bouton 4"
Button:
size_hint_y: 0.4
text: "bouton 5"
Button:
size_hint_y: 0.3
text: "bouton 6"
Button:
text: "bouton 7"
PageLayout
pagelayout.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import kivy
kivy.require('1.8.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (1120, 630)
class PagelayoutApp(App):
def build(FloatLayout):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
PagelayoutApp().run()
pagelayout.kv
#:kivy 1.8.0
PageLayout:
Button:
text: 'page1'
Button:
text: 'page2'
Button:
text: 'page3'
StackLayout
stacklayout.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import kivy
kivy.require('1.8.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (1120, 630)
class StacklayoutApp(App):
def build(FloatLayout):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
StacklayoutApp().run()
stacklayout.kv
#:kivy 1.8.0
StackLayout:
spacing: 10
padding: 10
orientation: 'tb-rl'
Button:
text: "bouton 1"
size_hint: 0.3, 0.5
Button:
text: "bouton 2"
size_hint: 0.2, 0.2
Button:
text: "bouton 3"
size_hint: 0.15, 0.2
RelativeLayout
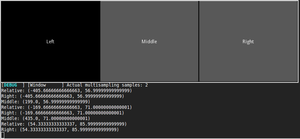 Retourne des coordonnées relatives
Retourne des coordonnées relatives
relativelayout.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import kivy
kivy.require('1.8.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (1120, 630)
class RelativelayoutApp(App):
def build(FloatLayout):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
RelativelayoutApp().run()
relativelayout.kv
#:kivy 1.8.0
BoxLayout:
Label:
text: 'Left'
Button:
text: 'Middle'
on_touch_down: print('Middle: {}'.format(self.to_local(*args[1].pos)))
RelativeLayout:
on_touch_down: print('Relative: {}'.format(self.to_local(*args[1].pos)))
Button:
text: 'Right'
on_touch_down: print('Right: {}'.format(self.to_local(*args[1].pos)))
ScatterLayout

 Permet de déplacer des widgets.
Permet de déplacer des widgets.
scatterlayout.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import kivy
kivy.require('1.8.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (1120, 630)
class ScatterlayoutApp(App):
def build(FloatLayout):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
ScatterlayoutApp().run()
scatterlayout.kv
#:kivy 1.8.0
FloatLayout:
ScatterLayout:
Label:
size_hint: 0.2, 0.2
text: 'Left'
Label:
size_hint: 0.2, 0.5
text: 'Middle'
ScatterLayout:
Label:
size_hint: 0.5, 0.2
text: 'Right'
Extrait des exemples de la documentation officielle
C'est bien pour voir ce que ça peut faire, mais ce ne sont pas des exemples simples.